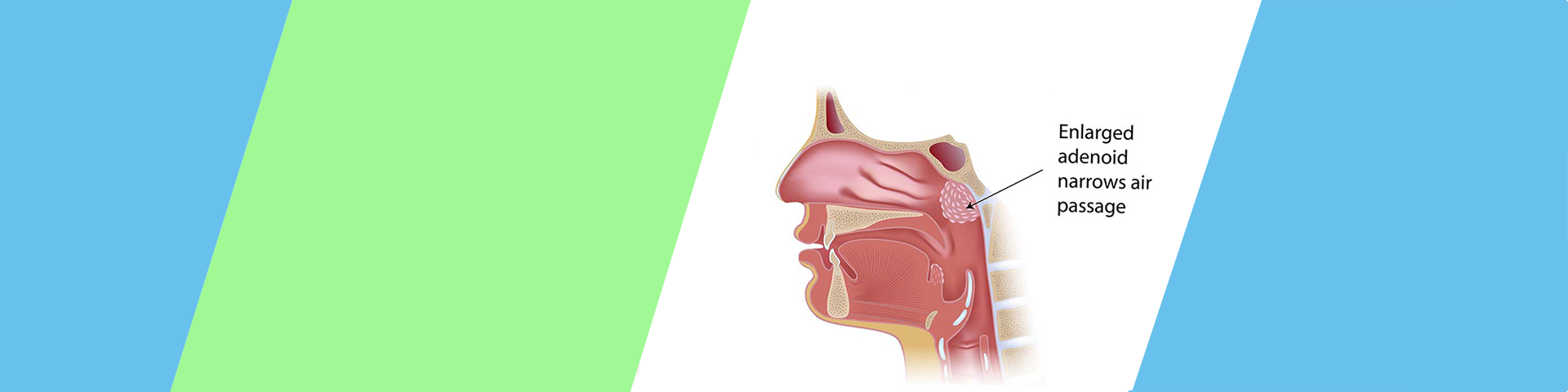
Adenoids are a small patch of tissue located at the top of the throat behind the nasal cavity. Adenoids are made of lymphoid tissue. Lymphoid tissue consists of connective tissue and white blood cells, especially lymphocytes. Lymphocytes make antibodies and play a role in immune response. They are like tonsils and located right above them. Your tonsils can be seen if you look at the back of your throat, but the adenoids aren’t directly visible. The adenoids can cause problems if they become enlarged. Fortunately, they’re not an essential part of the immune system, and they can generally be treated by removing them. Problem related to adenoids are usually seen in children
-
Symptoms
- Nasal congestion or stuffiness
- Difficulty breathing through the nose
- Snoring
- Breathing through the mouth
- Sleep disturbances, such as sleep apnea
- Chronic ear infections
- Sore throat
- Bad breath
- Difficulty swallowing or eating
- Speech problems
-
Causes
- Enlarged adenoids due to ear & upper respiratory infections
- Allergies
- Genetics
- Immunodeficiency disorders
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
Complications
Complications of Adenoids include:
Chronic ear infections (otitis media)
Sinus infections (sinusitis)
Breathing problems during sleep (sleep apnea)
Recurrent or persistent sore throat
Middle ear fluid accumulation (serous otitis media)
Speech and language delays
Dental problems, including malocclusion
Difficulty swallowing or eating
Obstructive sleep-disordered breathing
Impaired growth and development
FAQ
Yes, in some cases, enlarged adenoids can interfere with normal speech and swallowing patterns, leading to speech difficulties or discomfort while eating. Addressing the underlying adenoid enlargement may help improve these issues.
It can sometimes be challenging to differentiate between symptoms caused by enlarged adenoids and those caused by other conditions. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a physical examination and possibly diagnostic tests, can help determine the underlying cause of the symptoms.
Untreated enlarged adenoids can lead to complications such as recurrent ear infections, chronic sinus infections, sleep disturbances, and potential developmental issues in children. It's essential to address symptoms promptly to prevent these complications.
Yes, enlarged adenoids can obstruct the airway, leading to snoring and, in some cases, obstructive sleep apnea in children. This can result in disrupted sleep, daytime fatigue, and other related symptoms.
Yes, enlarged adenoids can contribute to dental issues such as malocclusion (misalignment of the teeth), open-mouth breathing, and an increased risk of cavities. Addressing adenoid enlargement may help improve dental health in some cases.
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate discomfort associated with enlarged adenoids. Additionally, using a humidifier, saline nasal sprays, or throat lozenge may provide relief. But it is advisable to do all the above in consultation with a pediatrician or a ENT(Otolaryngistologist)
Yes, allergies can exacerbate symptoms of enlarged adenoids by causing inflammation and swelling of the adenoid tissue. Managing allergies through avoidance of triggers and appropriate medications may help reduce adenoid-related symptoms.
Enlarged adenoids are more commonly seen in children, but they can occur in adults as well. However, adenoid tissue tends to shrink with age, so adenoid-related symptoms are less common in adults compared to children.
Adenoidectomy is generally considered safe and effective, but potential long-term consequences may include changes in voice quality, alterations in nasal airflow patterns, and rare complications such as regrowth of adenoid tissue.
Preparing a child for adenoidectomy surgery involves explaining the procedure in age-appropriate language, addressing any fears or concerns they may have, and providing support and reassurance throughout the process. Your healthcare provider can offer guidance on how to best prepare your child for surgery.