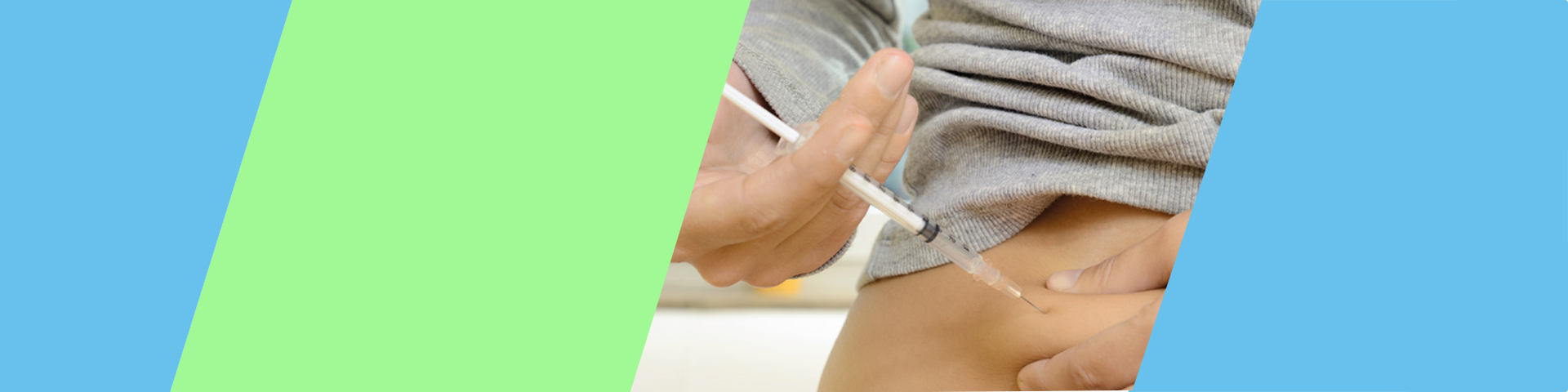
Diabetes mellitus is a condition defined by persistently high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. There are several types of diabetes. The two most common are called type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. During digestion, food is broken down into its basic components. Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, primarily glucose. Glucose is a critically important source of energy for the body's cells. To provide energy to the cells, glucose needs to leave the bloodstream and get inside the cells. An organ in the abdomen called the pancreas produces a hormone called insulin, which is essential to helping glucose get into the body's cells. In a person without diabetes, the pancreas produces more insulin whenever blood levels of glucose rise (for example, after a meal), and the insulin signals the body's cells to take in the glucose. In diabetes, either the pancreas's ability to produce insulin or the cells' response to insulin is altered.
-
Symptoms
- Polyuria (Frequent Urination)
- Polydipsia (Excessive Thirst)
- Polyphagia (Increased Hunger)
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Fatigue and Weakness
- Blurred Vision
- Slow Healing of Wounds
- Recurrent Infections
- Tingling or Numbness in Hands or Feet (Neuropathy)
- Erectile Dysfunction (in Men)
-
Causes
- Type 1 Diabetes: Autoimmune Destruction of Beta Cells
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin Resistance and Beta Cell Dysfunction
- Gestational Diabetes: Insulin Resistance during Pregnancy
- Prediabetes: Impaired Glucose Tolerance
- Genetic Factors
- Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle
- Pancreatic Disorders
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Medications or Chemicals
- Other Health Conditions (e.g., Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
Complications
Complications of Diabetes Mellitus include:
Cardiovascular Disease
Nephropathy (kidney disease)
Neuropathy (Nerve Damage)
Retinopathy (Eye Damage)
Diabetic Foot Complications
Skin Conditions
Dental Issues
Sexual Dysfunction
Gastroparesis (Delayed Stomach Emptying)
Mental Health Disorders
FAQ
Depending on the type of medication prescribed, side effects may include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), gastrointestinal discomfort, weight gain, or allergic reactions. It's essential to discuss potential side effects and how to manage them with your healthcare provider.
During illness or travel, managing diabetes may require adjustments to medication, monitoring blood sugar levels more frequently, staying hydrated, and carrying necessary supplies. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on managing diabetes during these situations.
Some individuals with diabetes find complementary therapies such as acupuncture, yoga, or certain dietary supplements helpful as adjuncts to conventional treatment. However, it's crucial to discuss these options with your healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and effective for you.
Diabetes during pregnancy (gestational diabetes) can increase the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby. Women with diabetes who are pregnant or planning to conceive should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage blood sugar levels and minimize risks to ensure a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Yes, diabetes mellitus can impact mental health and cognitive function, leading to increased risk of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. It's essential to prioritize mental well-being and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider for appropriate support and management.
Preventive measures for diabetic foot complications include regular foot inspections, proper foot care (keeping feet clean and moisturized), wearing comfortable shoes, avoiding walking barefoot, managing blood sugar levels, and promptly addressing any foot injuries or abnormalities.
Diabetes mellitus significantly increases the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and other health conditions. Managing diabetes effectively through lifestyle changes and medical treatment can help reduce these risks.
There are various resources and support services available, including diabetes education programs, support groups, online forums, and educational materials provided by healthcare organizations and advocacy groups. Your healthcare provider can help connect you with these resources.
Yes, diabetes management should be personalized to your individual needs, preferences, and lifestyle factors. Your healthcare provider can work with you to develop a comprehensive management plan that addresses your specific goals and challenges.
Long-term goals of diabetes management include maintaining blood sugar levels within target ranges, preventing complications, improving overall health and well-being, and enhancing quality of life. Working closely with your healthcare provider, adopting healthy habits, and staying informed about diabetes management strategies can help you achieve these goals.