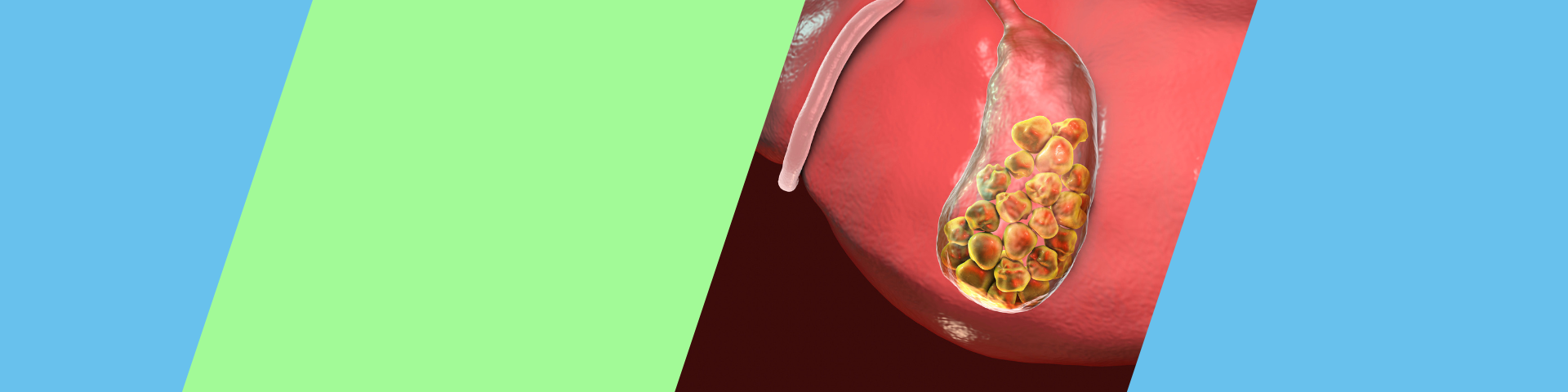
Your gallbladder is a small organ in your upper right abdomen, below your liver. It's a pouch that stores bile, a green-yellow liquid that helps digestion. Issues with your gallbladder typically occur when something, like a gallstone, blocks its bile duct. Gallstones are deposits of digestive fluid made of solidified substances found in bile, like cholesterol. They are common and may or may not produce symptoms. People with symptoms usually need to have their gallbladders taken out.
-
Symptoms
- A high temperature
- Rapid heartbeat
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Itchy skin
- Diarrhea
- Chills
- Confusion
- A loss of appetite
-
Causes
- Excess Cholesterol
- Bile Imbalance
- Poor Gallbladder Emptying
- Obesity
- Rapid Weight Loss
- Genetics:
- Certain Medical Conditions
- Certain Medications
- Age and Gender
- Dietary Factors
Complications
Complications of Gall Stones include:
Gallstone Pancreatitis
Cholecystitis
Cholangitis
Biliary Colic
Gallstone Ileus
Gallbladder Cancer
Empyema
Gallstone Abscess
Acute Pancreatitis
Mirizzi Syndrome
FAQ
Yes, gallstones can lead to complications such as cholecystitis, pancreatitis, or bile duct obstruction, even if they are not causing symptoms. Therefore, treatment may be recommended even for asymptomatic gallstones, mainly if other risk factors exist.
Yes, risk factors include being female, being overweight or obese, having a sedentary lifestyle, having a family history of gallstones, and certain medical conditions like diabetes or liver disease.
Yes, consuming high-fat or greasy foods, spicy foods, or large meals can sometimes trigger symptoms in gallstone individuals. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods may help manage symptoms.
Gallstones are relatively common during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased cholesterol levels in the bile. Most gallstone-related symptoms can be managed conservatively during pregnancy, but surgical treatment may be considered in severe cases, especially after delivery.
Medications used to dissolve gallstones, may cause side effects like diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, or an allergic reaction. Patients should be closely monitored for side effects while on medication therapy.
Applying heat to the abdomen, resting comfortably, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers may help alleviate mild gallstone-related symptoms. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, medical attention should be sought.
Patients experiencing severe or persistent symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, or vomiting should seek immediate medical attention, as these could indicate complications that require urgent treatment.
While specific alternative therapies like acupuncture or herbal remedies may help for symptom management, their effectiveness for treating gallstones is not well-established, and patients should discuss their use with a healthcare provider.
Yes, gallstones can recur, mainly if underlying risk factors are not addressed. To help prevent recurrence, patients should maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management.
Recovery time after gallbladder surgery varies from person to person but generally involves a few days of hospitalization followed by rest at home. Patients should follow post-operative instructions, including dietary guidelines and activity restrictions, to facilitate healing and minimize complications.