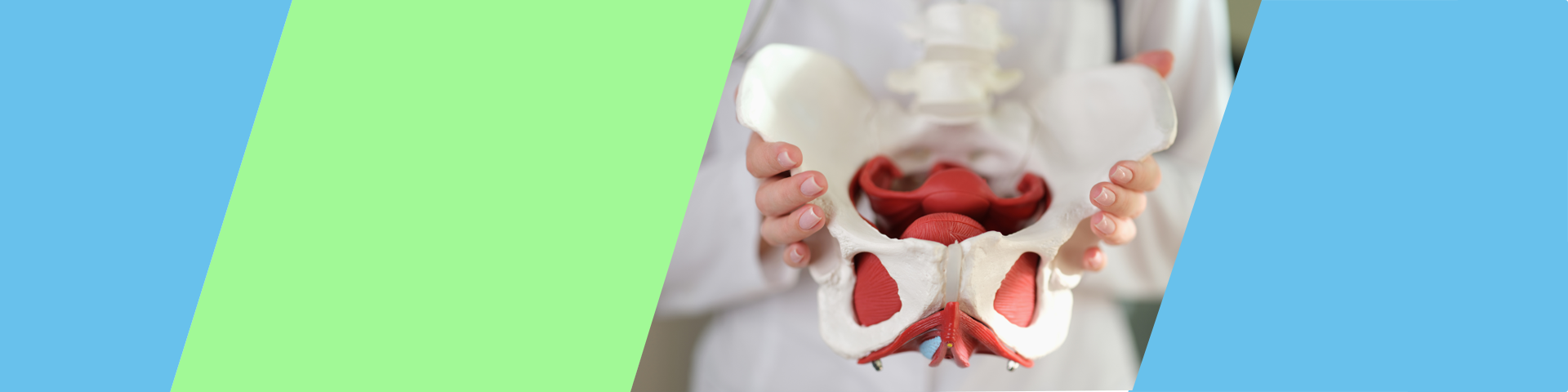
The perineum lies near several nerves, muscles, and organs, so it’s not uncommon to feel pain in this area. Injuries, urinary tract issues, infections, and other conditions can cause perineum pain. The perineum refers to the area between the anus and genitals, extending from either the vaginal opening to the anus or from the scrotum to the anus.
-
Symptoms
- Pain
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Difficulty Urinating
- Difficulty Defecating
- Bleeding
- Difficulty Sitting or Walking
- Numbness or Tingling
- Difficulty with Sexual Activity
- Infection
-
Causes
- Trauma
- Childbirth
- Medical Procedures
- Sexual Activity
- Straddle Injuries
- Sports Injuries
- Repetitive Stress
- Child Abuse or Assault
- Medical Conditions
- Genitourinary Disorders
Complications
Complications of Perineal Injury include:
Infection
Delayed Healing
Chronic Pain
Scarring
Erectile Dysfunction
Urinary Incontinence
Fecal Incontinence
Sexual Dysfunction
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
Psychological Distress
FAQ
Perineal injury refers to damage or trauma to the area between the anus and the genital organs. Common causes include trauma, childbirth, medical procedures, sexual activity, and sports injuries.
Symptoms of a perineal injury may include pain, swelling, bruising, difficulty urinating or defecating, bleeding, difficulty sitting or walking, numbness or tingling, and signs of infection.
If you suspect a perineal injury, it's essential to seek medical attention promptly. Avoid further trauma to the area and follow any first aid measures recommended by your healthcare provider.
Diagnosis of a perineal injury typically involves a physical examination of the affected area, assessment of symptoms, and may include imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI to evaluate the extent of the injury.
Untreated perineal injuries can lead to complications such as infection, delayed healing, chronic pain, scarring, erectile dysfunction, urinary or fecal incontinence, sexual dysfunction, and psychological distress.
Treatment for perineal injuries depends on the severity and type of injury but may include wound care, pain management, antibiotics for infection, surgical repair, physical therapy, and counseling for psychological support.
The healing time for a perineal injury varies depending on the extent of the injury, treatment received, and individual factors such as overall health and compliance with medical advice. Minor injuries may heal within a few weeks, while more severe injuries may take longer.
During the healing process, it's essential to follow any recommendations provided by your healthcare provider, such as avoiding activities that could aggravate the injury, maintaining proper hygiene, and keeping the area clean and dry.
Some individuals may experience long-term effects or complications from a perineal injury, such as chronic pain, sexual dysfunction, or pelvic floor dysfunction. Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider can help monitor any ongoing issues.
Preventing perineal injuries involves taking precautions such as using proper safety equipment during sports activities, practicing safe sexual practices, seeking prompt medical attention for any symptoms of infection or trauma, and maintaining overall good health and hygiene.