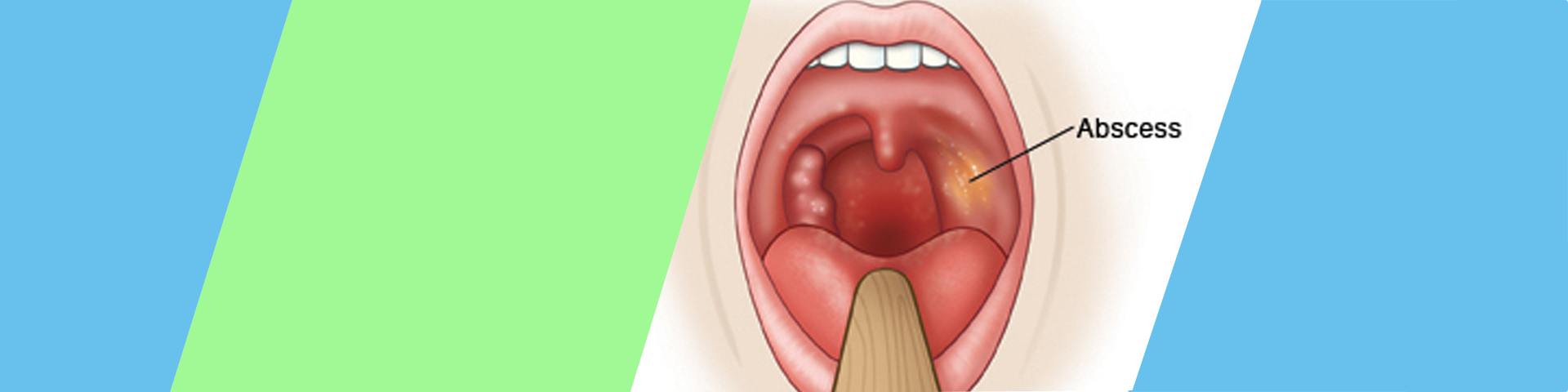
A peritonsillar abscess is a pus-filled pocket that forms near one of your tonsils. It’s usually a complication of tonsillitis and is often caused by the same bacteria that causes strep throat. Symptoms include severe pain, swollen tonsils and swollen lymph nodes. Treatments include needle aspiration and tonsillectomy.
-
Symptoms
- Sore Throat
- Fever
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
- Pain on One Side of the Throat
- Swollen Tonsils
- Redness and Inflammation of the Tonsils
- Difficulty Opening the Mouth (Trismus)
- Bad Breath (Halitosis)
- Earache on the Affected Side
- Muffled Voice
-
Causes
- Tonsillitis
- Bacterial Infection
- Streptococcus bacteria
- Complications from Untreated Tonsillitis
- Spread of Infection to Surrounding Tissues
- Peritonsillar Cellulitis
Complications
Complications of Peritonsillar Abscess include:
Airway Obstruction
Septicemia (Blood Infection)
Ludwig's Angina
Mediastinitis
Lemierre's Syndrome
Retropharyngeal Abscess
Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Spread of Infection to Surrounding Structures
Difficulty Eating and Drinking
Chronic Recurrence of Abscesses
FAQ
Proper treatment of tonsillitis and prompt medical attention for symptoms suggestive of an abscess can help prevent its formation. Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding close contact with individuals who have contagious throat infections may also reduce the risk.
The abscess itself is not contagious, but the underlying bacterial infection, such as streptococcal infection, can be transmitted through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing. Therefore, it's essential to practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of infection.
Seek medical attention promptly if you experience severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, fever, or swelling of the throat. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications.
Yes, while most cases resolve with proper treatment, there is a risk of recurrence, especially if the underlying cause, such as chronic tonsillitis, is not addressed. Recurrence may necessitate further medical evaluation and management.
Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke, and practicing proper hand hygiene can help reduce the risk of recurrent infections that may lead to peritonsillar abscess formation.
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience worsening symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, severe neck pain, or persistent fever, as these could indicate complications that require urgent medical attention.
While the symptoms and treatment for peritonsillar abscesses are generally similar in children and adults, children may be at a higher risk of complications due to their smaller airways. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment are crucial in children to prevent severe complications.
Home remedies, such as gargling with warm salt water or using throat lozenges, may provide temporary relief of symptoms but should not be relied upon as sole treatment. Prompt medical evaluation and appropriate treatment by a healthcare professional are essential for managing peritonsillar abscesses effectively.