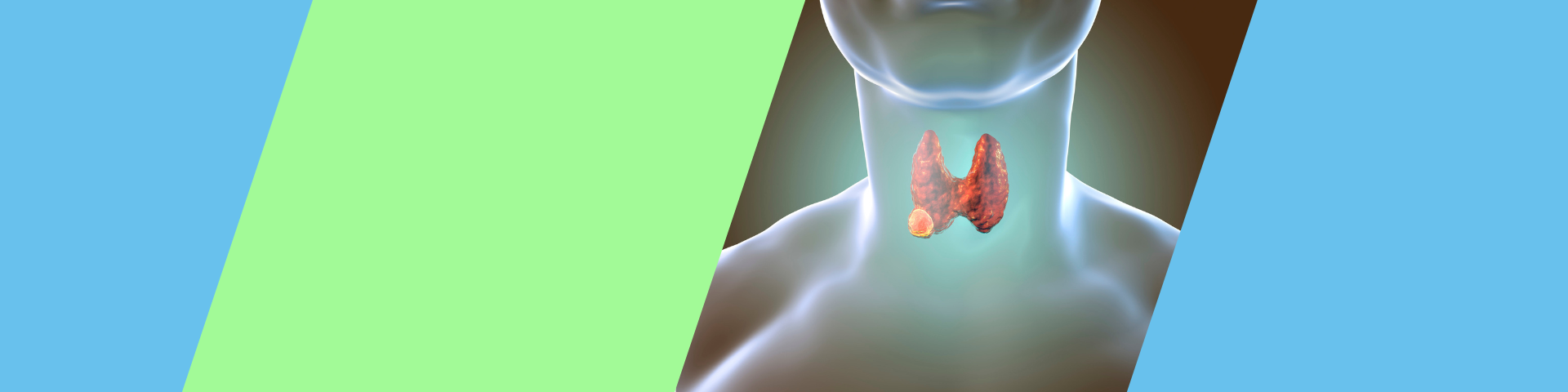
Thyroid cancer is a growth of cells that start in the thyroid. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, just below Adam's apple. The thyroid produces hormones that regulate heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature and weight. Thyroid cancer might not cause any symptoms at first. But as it grows, it can cause signs and symptoms, such as swelling in your neck, voice changes and difficulty swallowing.
-
Symptoms
- A lump in your throat
- Swelling or nodules in your neck
- Neck pain, starting in front and sometimes moving up to the ears
- Hoarseness
- voice changes that don’t go away
- Difficulty swallowing
- Trouble breathing
- Persistent cough
-
Causes
- Genetic factors
- Radiation exposure
- Gender
- Age
- Iodine deficiency or excess
- Thyroid nodules
- Autoimmune thyroid disease
- Environmental factors
- Dietary factors
- Lifestyle factors
Complications
Complications of Thyroid Cancer include:
Metastasis
Recurrence
Compromised thyroid function
Vocal cord paralysis
Damage to nearby structures
Lymphedema
Complications of radioactive iodine therapy
Psychosocial impact
Impact on fertility
Secondary cancers
Osteoporosis
Cardiovascular complications
Nutritional deficiencies
Cosmetic changes
FAQ
There are no known ways to prevent thyroid cancer entirely. However, avoiding exposure to radiation, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and promptly addressing any thyroid nodules or abnormalities may help reduce the risk.
Thyroid cancer can be classified into several types, including papillary thyroid carcinoma (the most common type), follicular thyroid carcinoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma, and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Each type has distinct characteristics and treatment approaches.
Genetic testing may be recommended in certain cases, especially if there is a family history of thyroid cancer or if specific genetic syndromes associated with thyroid cancer are suspected. Your healthcare provider can advise you on whether genetic testing is appropriate for your situation.
The timing of treatment initiation depends on factors such as the type and stage of thyroid cancer, the presence of any symptoms or complications, and the individual's overall health. Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a treatment plan and determine the appropriate timing for starting treatment.
Thyroid cancer itself typically does not affect fertility. However, certain treatments for thyroid cancer, such as radioactive iodine therapy or high-dose radiation, may temporarily or permanently affect fertility. It's important to discuss any concerns about fertility with your healthcare provider before starting treatment.
In most cases, no significant dietary or lifestyle changes are necessary after thyroid cancer treatment. However, maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, and adhering to any medication regimen prescribed by your healthcare provider are important for overall health and well-being.
Managing side effects or complications of thyroid cancer treatment may involve medications to alleviate symptoms (such as pain or nausea), lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, or additional medical interventions as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Many people treated for thyroid cancer can lead normal, fulfilling lives after completing treatment. However, the experience may vary depending on individual circumstances, treatment outcomes, and any lingering effects of cancer or its treatment. It's essential to communicate openly with your healthcare team and seek support as needed.
Yes, regular monitoring and surveillance are typically recommended after thyroid cancer treatment to detect any signs of recurrence or progression early. This may involve periodic physical examinations, imaging tests, blood tests, and thyroid function tests as directed by your healthcare provider.
Advocating for yourself as a thyroid cancer patient involves staying informed about your condition, actively participating in treatment decisions, communicating openly with your healthcare team, seeking support from loved ones or support groups, and advocating for your needs and preferences throughout the treatment process.