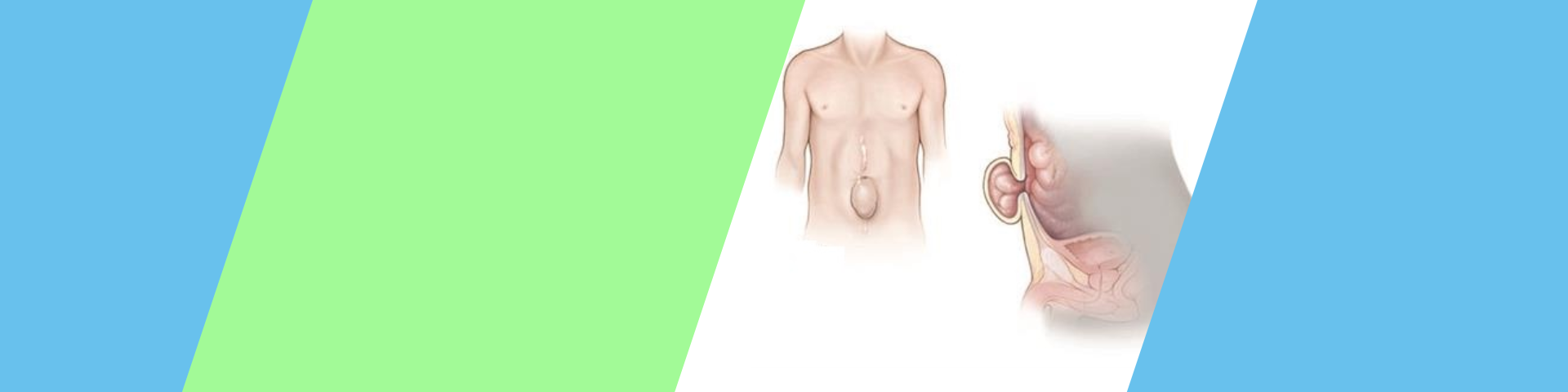
A ventral hernia is a bulge of tissues through an opening of weakness within your abdominal wall muscles. It can occur at any location on your abdominal wall. In a strangulated ventral hernia, intestinal tissue gets tightly caught within an opening in your abdominal wall. This tissue can’t be pushed back into your abdominal cavity, and its blood flow is cut off. This type of ventral hernia is an emergency requiring surgery.
-
Symptoms
- Mild discomfort in your abdominal area
- Pain in your abdomen
- Outward bulging of skin or tissues in your abdominal area
- Nausea
- Vomiting
-
Causes
- Previous Abdominal Surgery
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Heavy Lifting
- Chronic Coughing or Sneezing
- Ascites
- Age
- Connective Tissue Disorders
- Chronic Constipation
- Genetic Predisposition
Complications
Complications of Ventral Hernia include:
Incarceration
Strangulation
Bowel obstruction
Pain and discomfort
Infection
Recurrence
Mesh-related complications
Seroma formation
Hematoma
Chronic pain syndrome
Cosmetic concerns
FAQ
Yes, untreated ventral hernias can lead to serious complications such as bowel obstruction, incarceration, and strangulation, which may require emergency medical intervention.
Signs of incarceration or strangulation include sudden severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, inability to pass gas or stool, and a visibly tender, firm, or discolored lump at the hernia site. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Certain exercises that put strain on the abdominal muscles, such as heavy weightlifting or intense abdominal crunches, should be avoided if you have a ventral hernia. Your doctor or physical therapist can provide guidance on safe exercises.
Pregnancy can potentially worsen a pre-existing ventral hernia due to increased abdominal pressure and stretching of the abdominal wall. It's important to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider if you're pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
While complications during pregnancy due to a ventral hernia are rare, it's essential to monitor the hernia closely and seek medical advice if you experience severe pain, changes in the hernia size or appearance, or any concerning symptoms.
It's recommended to wait until after you've completed your family planning, and your body has had time to recover from childbirth before undergoing ventral hernia repair surgery. Your doctor can provide personalized recommendations based on your individual circumstances.
Yes, ventral hernias can occur in infants and children, typically due to a weakness in the abdominal wall present at birth (congenital hernia) or factors such as obesity, chronic coughing, or abdominal trauma.
Treatment approaches for ventral hernias in children may differ from those in adults and often involve observation with the possibility of surgical repair if the hernia persists or becomes symptomatic. Your child's pediatrician or a pediatric surgeon can provide specific guidance.
Depending on the size and severity of the hernia, it may be advisable to avoid certain high-impact activities or exercises that could exacerbate the hernia. Your doctor or physical therapist can recommend safe exercises and modifications based on your individual situation.
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fiber and staying hydrated can help prevent constipation and reduce strain on the abdominal muscles, potentially easing symptoms associated with ventral hernias. However, specific dietary recommendations should be discussed with your healthcare provider.